Domain Name¶
You will need a domain name as Saltbox apps are only accessed via https://appname.yourdomain.com (see Accessing Saltbox Apps). The steps below will help you set up a domain and DNS settings for use with Saltbox.
Ports are [for the most part] bound only to the internal saltbox docker network, which means they are not visible on the host; you won't be able to connect externally to the apps using IP:PORT.
1. Domain Provider¶
Get a domain name from any domain name registry (e.g. Namecheap, Godaddy, Namesilo, etc).
If you already have one, you may skip this step.
Note: Free domain name providers, such as Freenom, do not support wildcard DNS settings, and paid domain names can be had for less than a dollar per year (see promo deals on various sites). However, you can add them to Cloudflare and not have to worry about it.
If you are planning to use the automatic Cloudflare integration, there are some top-level domains [TLDs] that will not work with it. Refer to this page.
As of 2020/07/26: "DNS API cannot be used for domains with .cf, .ga, .gq, .ml, or .tk TLDs."
2. DNS Setup¶
Pick one of the setups below. Your choice will depend on whether you meet certain criteria, as listed under the "Notes" section.
i. Wildcard DNS Setup¶
Notes:
-
For DNS providers that allow wildcards.
-
For [[Saltbox install type|Basics: Saltbox Install Types]].
Steps:
Created an A Record for your subdomains with * for host and set the value to your server IP address.
| Type | Host | Value | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Record | * | Server IP Address | 300 |
Example
Namecheap > Domain List > Manage > Advanced DNS > Add New Record > A Record > `*` for Host > Server IP for Value. ii. Non-Wildcard DNS Setup¶
Notes:
-
For DNS providers that do not allow wildcards (e.g. Freenom).
-
For Cloudflare users.
Note: if you provide a Cloudflare email and API Key in your settings, the Saltbox installer will set this up for you automatically, provided you enter a top-level domain in the settings [i.e. DOMAIN.TLD, not WHATEVER.DOMAIN.TLD]
You will need to create A Records for all Saltbox subdomains.
| Type | Host | Value | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Record | plex | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | tautulli | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | jackett | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | radarr | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | sonarr | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | rutorrent | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | nzbget | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | nzbhydra2 | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | organizr | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | portainer | Saltbox IP Address | 300 |
You will need to create A Records for both IP addresses (Media and Feeder boxes) and set them to their respective subdomains.
Mediabox
| Type | Host | Value | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Record | plex | Mediabox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | tautulli | Mediabox IP Address | 300 |
Feederbox
| Type | Host | Value | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A Record | jackett | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | radarr | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | sonarr | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | rutorrent | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | nzbget | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | nzbhydra2 | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | organizr | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
| A Record | portainer | Feederbox IP Address | 300 |
Cloudflare¶
Intro¶
Cloudflare a service that, among other things, protects and accelerates a wide network of websites. By being the "man in the middle", it can act like a free DNS provider.
Saltbox makes adding subdomains to Cloudflare's DNS settings a breeze via automation. All you need is the API key.
Note that there are some top-level domains [TLDs] that will not work with this automation. Refer to this page.
As of 2020/07/26: "DNS API cannot be used for domains with .cf, .ga, .gq, .ml, or .tk TLDs."
Although Cloudflare is not required for Saltbox, it is still recommended because:
-
DNS changes propagate almost instantly (a lot faster than a domain provider's DNS service).
-
Hide your server's IP behind Cloudflare's.
-
Makes setting up Mediabox / Feederbox a lot quicker.
-
Allows for automated setup of subdomains for Saltbox add-on apps.
-
It's free.
Note: Saltbox does not enable CDN / Proxy by default, but you may do so yourself after installing Saltbox (see section [[below|Prerequisites: Cloudflare#post-setup]]).
Sign Up¶
-
Sign up for a free Cloudflare account.
-
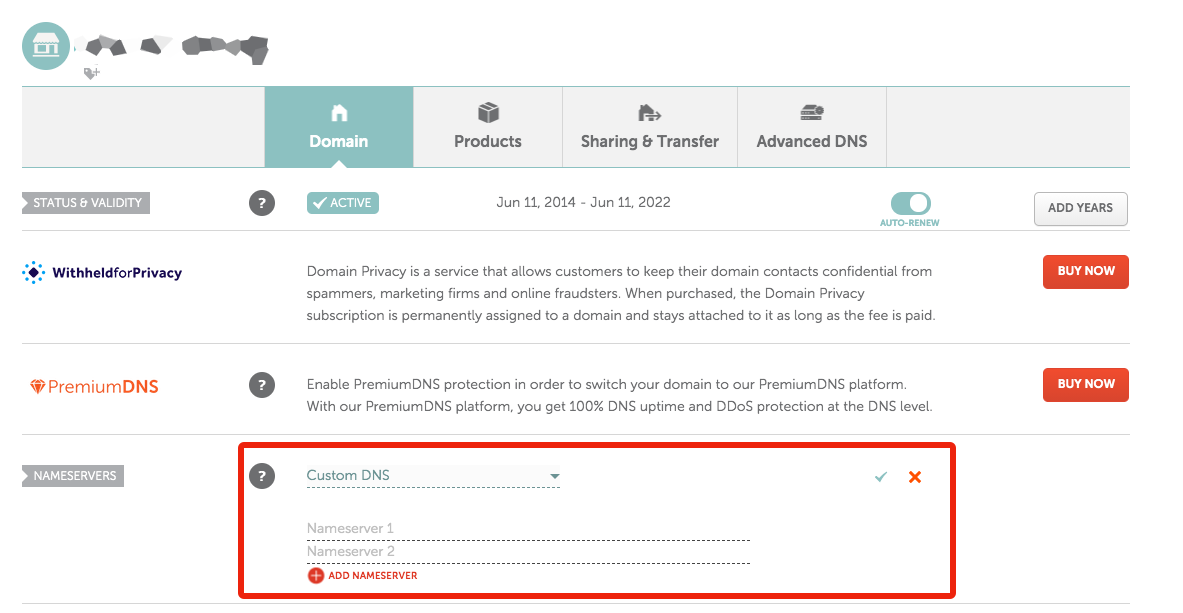
On your Domain Registrar's website (e.g. GoDaddy, Namecheap, etc), set the Name Servers to what Cloudflare instructs you to.
"Dashboard" -> your domain.tld -> "Manage" -> "Name Servers" -> "Custom DNS" -> add the nameservers in.
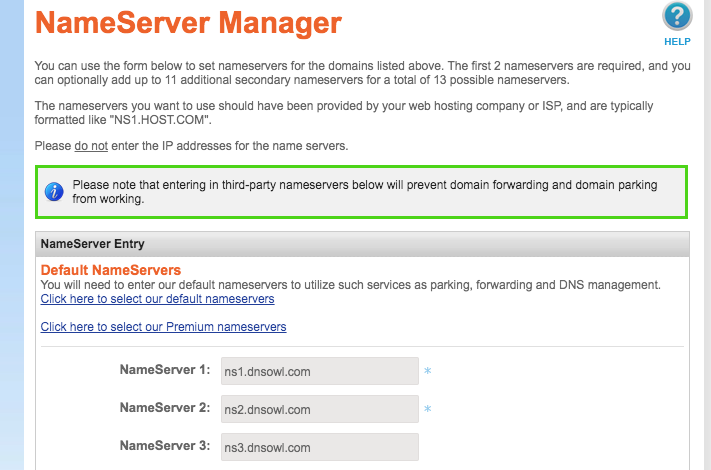
"Manage My Domains" -> your domain.tld -> "NameServers" -> "Change" -> add the nameservers in.
Setup¶
-
Go to Cloudflare.com.
-
Here you will see that your domain will have an "Active" status. Click on your domain to continue.
-
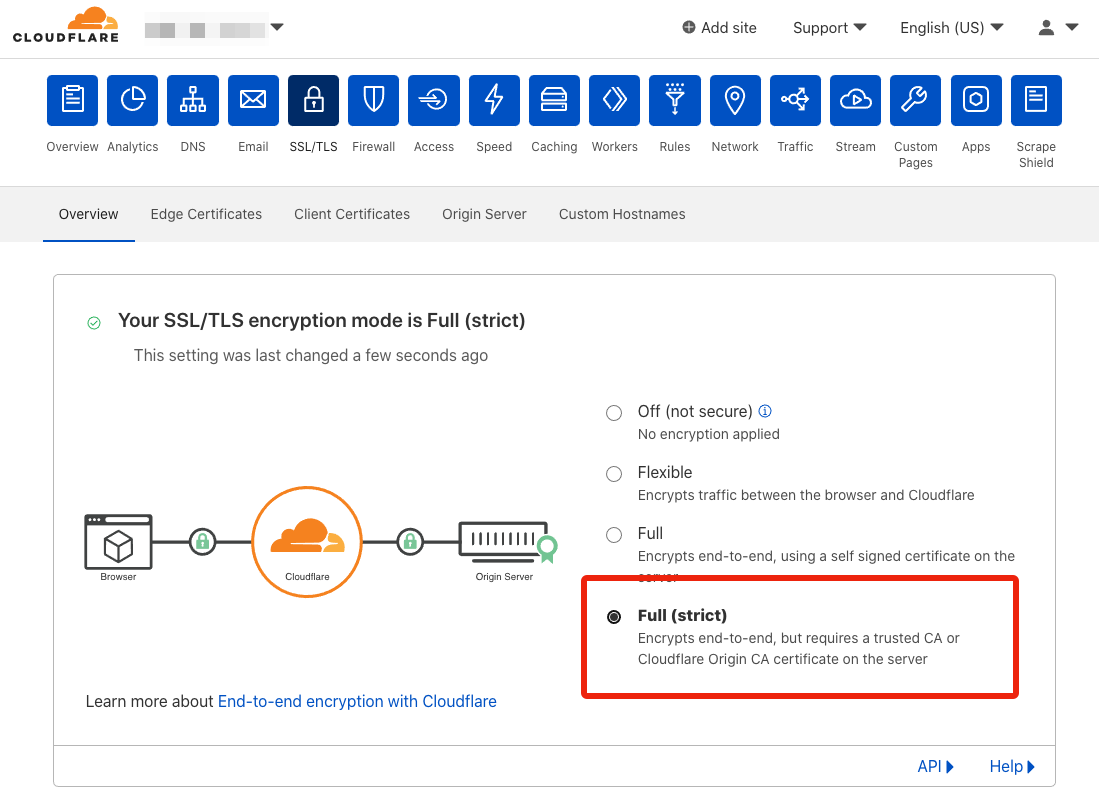
Click the SSL/TLS tab.
-
Set SSL to
Full (strict).
Cloudflare API Key¶
-
Go to Cloudflare.com.
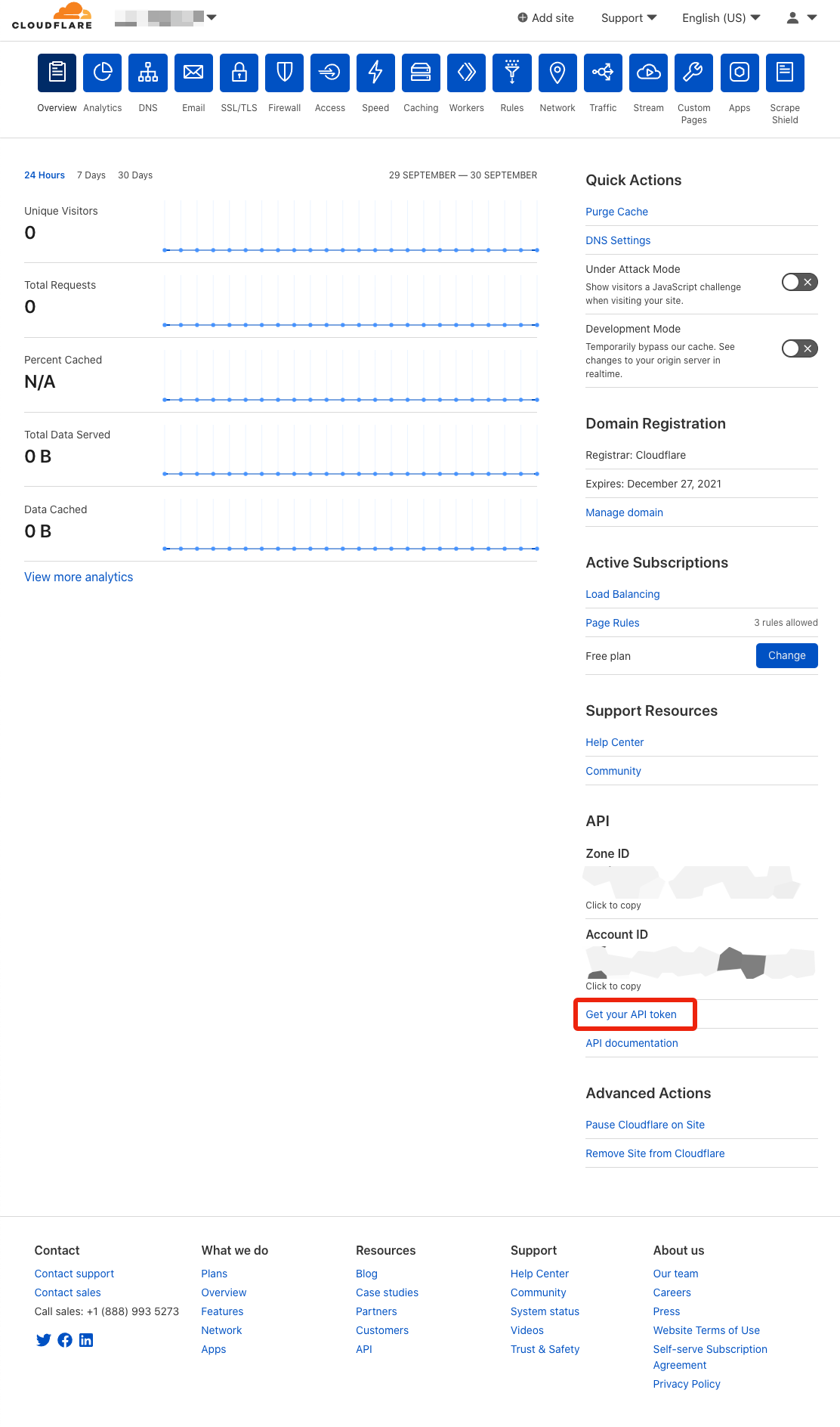
-
Click the Overview tab.
-
Click Get your API token.
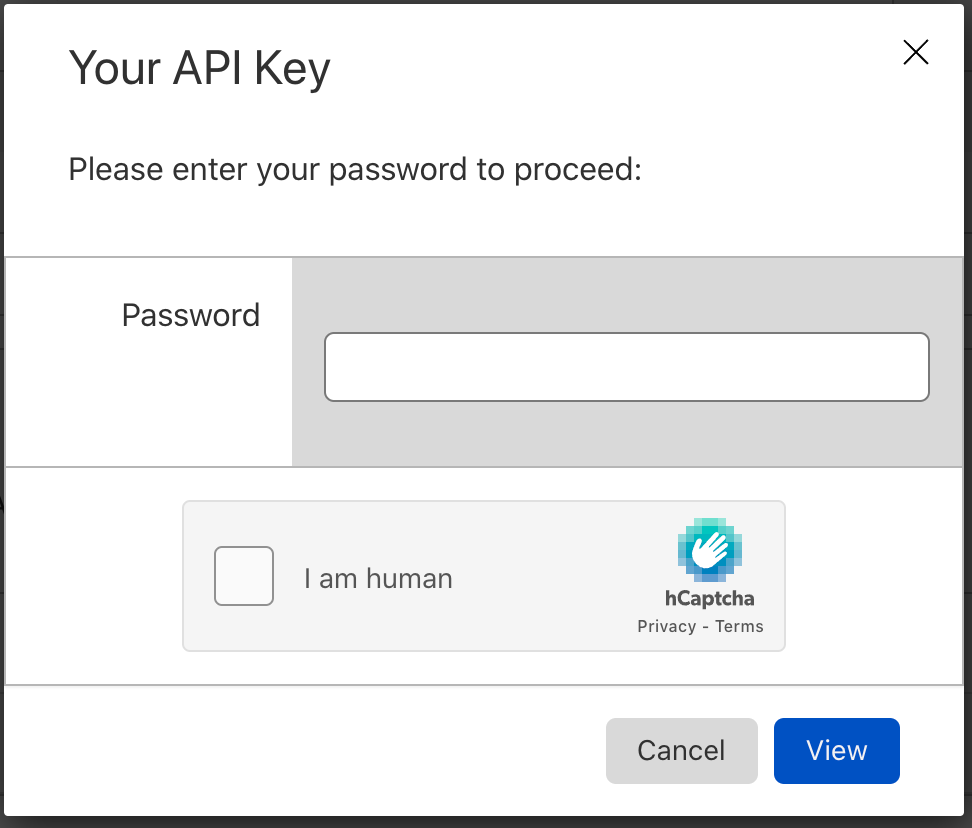
- Under API Keys and then Global API Key click View.

- On the login popup, type in your password and click View.
- Save your API key.

Post-Setup¶
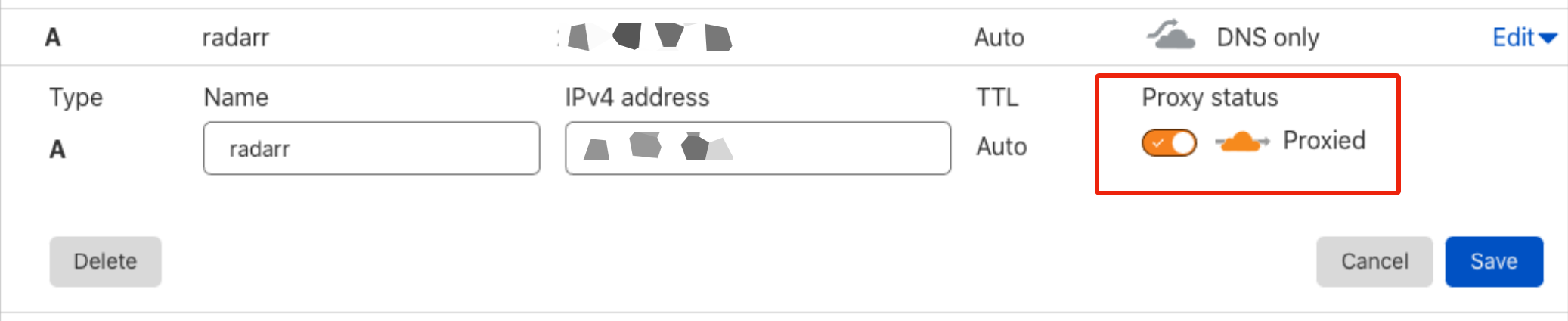
After Saltbox has added in the subdomains, you may go back in and turn on CDN for for them if you like. NOte, however, that enabling proxying on your plex or emby subdomains [or more generally proxying large amounts of non-HTML content] is against Cloudflare TOS and may end up getting your Cloudflare account banned.
Do this AFTER all your certs have been assigned and you have confirmed that all the Saltbox app sites are loading OK.
This also applies to any app/subdomains you add in the future - wait till after you get certs before enabling CDN.
Note 1: Leave the subdomains saltbox, mediabox, and feederbox as DNS Only, as they were created to reach your servers directly and not behind a CDN proxy (i.e. they need to resolve to the server's IP and not Cloudflare's).
Note 2: If you enable proxying on plex/emby subdomains despite it being against TOS, you may find that performance suffers badly.
You can do this by:
-
Going to Cloudflare.com.
-
Clicking the DNS tab.
-
Find the subdomain of interest.
-
Under "Status", click the switch next to the gray cloud icon (i.e.
DNS Only) to switch to an orange one (i.e.DNS and HTTP proxy (CDN)).